gyratory crusher china
Gyratory Crushers: The Chinese Manufacturing Powerhouse in Global Mining
The gyratory crusher, a cornerstone technology for primary crushing in large-scale mining and aggregate operations, has seen its global manufacturing landscape significantly shaped by China's industrial ascent. Chinese manufacturers have evolved from being followers to becoming major global suppliers, offering a comprehensive range of gyratory crushers that combine competitive pricing, rapid production capacity, and increasingly sophisticated technology. This article provides an overview of China's role in the gyratory crusher market, examining its product offerings, technological progress, and the tangible value proposition it presents to the global mining industry.
Chinese-made gyratory crushers are available in various sizes and configurations to meet different duty requirements, from robust machines for hard rock mining to high-capacity models for aggregate production. Key players include state-owned heavy machinery groups and large publicly traded engineering firms with decades of experience. The core value proposition often centers on cost-effectiveness and delivery speed without completely sacrificing performance for mid-range applications.
A common point of discussion is how these crushers compare with established Western brands (e.g., Metso Outotec, FLSmidth) in critical operational aspects. The following table outlines general contrasts based on industry reports and user feedback:
| Feature | Typical Chinese Gyratory Crusher | Typical Premium Western Brand Crusher |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Capital Cost | Significantly lower | Higher |
| Lead Time | Generally shorter | Often longer |
| Material & Component Quality | Variable; improving but can use more standard grades | Consistently high; uses premium alloys & bearings |
| Technological Features | Standard automation; catching up on smart features | Advanced automation, predictive analytics, smart wear monitoring |
| After-Sales & Global Support | Expanding but can be inconsistent regionally | Extensive, well-established global network |
| Lifecycle Cost (TCO) | Potentially higher for very abrasive/ demanding sites due to wear part life & downtime | Often optimized for lower TCO in severe duty through durability |
Real-World Application Case: Iron Ore Processing Plant in Southeast Asia.jpg)
A prominent real case involves a large iron ore processing plant in Southeast Asia that commissioned a primary crushing station using a Chinese-made 60-89 gyratory crusher equivalent around 2018. The decisive factors were the project's tight budget constraints and an aggressive construction timeline. The Chinese supplier provided a complete design, manufacturing, and commissioning package at approximately 70% of the cost quoted by Western alternatives, with delivery achieved four months faster. Post-commissioning, the crusher met the required throughput of over 5,000 t/h. However, the plant reported higher-than-expected wear rates on concaves and mantles under the highly abrasive ore conditions, leading to more frequent shutdowns for liner changes than initially projected. This case illustrates the trade-off: significant upfront savings enabled the project's launch but resulted in higher ongoing operational expenses and availability considerations—a classic TCO scenario where detailed duty analysis is crucial.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Are Chinese gyratory crushers simply copies of Western designs?
While early models were often based on licensed or expired patent designs from last century, leading Chinese manufacturers now invest heavily in independent R&D. They develop their own crushing chamber profiles (like Z-shaped or C-shaped chambers), mantle designs, and hydraulic control systems. Modern units are not direct copies but engineered products that meet international performance standards like GB (Chinese National Standard) and often reference ISO norms.
2. What is the main advantage of choosing a Chinese gyratory crusher?
The primary advantage is cost-effectiveness on a capital expenditure (CAPEX) basis. For greenfield projects with strict budget limits or where rapid equipment deployment is critical to project timelines, Chinese crushers offer a viable solution to secure primary crushing capacity without the premium price tag.
3. What are potential risks or drawbacks?
Key risks relate to long-term reliability under severe duty and after-sales support. Wear part life may be shorter in highly abrasive applications, increasing operating costs. Furthermore, while major Chinese suppliers have improved their international service networks, localized technical expertise and spare parts inventory may not be as robust or responsive as those of entrenched Western competitors in remote mining locations.
4. Can I get genuine wear parts from sources other than the OEM?
Yes, but with caution. The aftermarket for compatible wear parts (concaves, mantles) for Chinese gyratory crushers is growing globally. Many third-party foundries produce these parts. However, quality varies dramatically. It is essential to vet alternative suppliers thoroughly through material certification (e.g., ASTM A128 manganese steel grades) and site references to avoid premature failure that can cause costly damage to the crusher.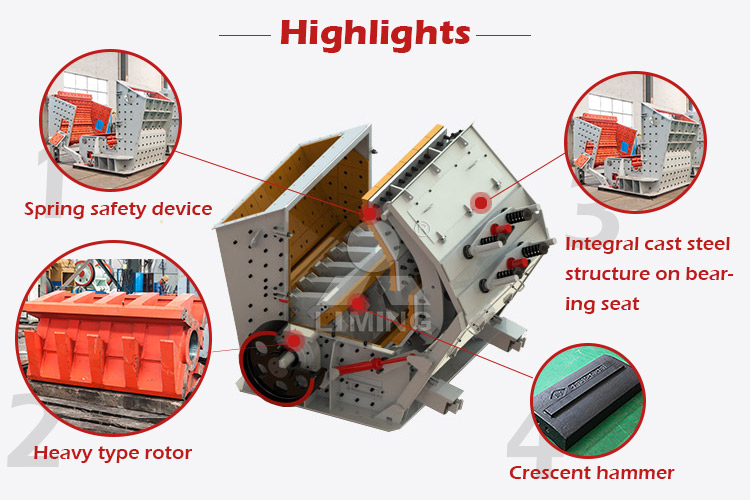
5. How do I ensure good after-sales service when buying a Chinese gyratory crusher?
Due diligence is paramount before purchase:
- Contractual Clarity: Insist on detailed service level agreements (SLAs) within the supply contract covering response times, technical support language(s), and spare parts delivery guarantees.
- Local Presence: Verify if the manufacturer or its authorized agent has engineers or a warehouse within your region.
- Reference Checks: Contact previous international clients of the specific manufacturer to inquire about their direct experience with installation support and long-term service reliability
